Research
My research in Exeter is about the doping of semiconductors (in particular GaN) with rare earth (in particular Erbium (Er)).
Rare
earth are very interesting for doping semi-conductors because of their f
electron shell that have a really special behavior. The f shell is very
contacted in rare earth and is shielded
by the valence electrons. Then, the electronic transitions that are
possible in between the f-shell are very weakly dependant of the surrounding of
the rare earth. It the rare earth electronic transition can be exited they will
induce the emission of light at a given wave length that is do not dependant of
the surrounding. The depending of the excitation it is possible to produce
infra-red light or visible light of different colors. In particular Er shows
transition in the infra-red at 1.52 mm that corresponds to the minimum of
adsorption of optic fiber, that is very suitable for opto-electronics.
Further
more the use of rare earth could also be a way to produce light with indirect
semi-conductors (like Si) that cannot produce efficiently light. Then, part of
my research is focused on understanding the structures than can give this light
production in Si.
Structure of Erbium defect in Si
Er co-doped with oxygen has
shown some huge increase of the light emission at room temperature.
Unfortunately, the interaction and structure that Er and O form in Si are still
not very well known but nevertheless are fundamental to understand how to get
an efficient light emitter.
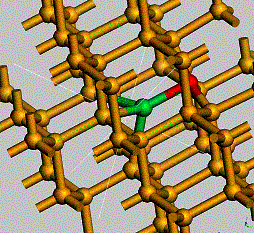
Er-O structure in Si
Structure of Rare Eaths in GaN
The
doping of hight gap semiconductor GaN with rare earth is a way to produce
efficient visible light emitter in particular around the blue color that would be
valuable both to produce laser for high density information storage or simply
to create array diodes for flat sceens. Nevertheless, the behavior of rare
earth inside GaN is not very well known. The understanding of the local Er
structure that can give rise to an efficient light emission is fundamental.
Rare Eaths defects interaction in GaN
Early calculation have shown that Rare Earths (RE) alone in GaN are electriacally inactive. We are then investigating the RE-defects complex in GaN that can induce efficient energy transfert to the RE and then gives a good light production yield. It finally should be possible to define the proper condition of growth and impurities from first principle calculations.
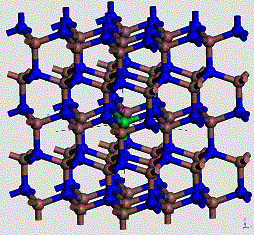
Er in GaN
You
can find here the last talk I gave at the E-MRS Strasbourg
(2003) for more detailed informations
The Exter physics theory group.
Contact: Jean-Sebastien Filhol (filhol@excc.ex.ac.uk)
Last revised: 25/08/2003