Imaging metal oxide nanoparticles in biological
structures with CARS microscopy
J. Moger, B. D. Johnston and C. R. Tyler.
Optics Express, 16 (5), 3408-3419, 2008.
The physiological and environmental effect of metal oxide nanoparticles is currently a topic of hot debate.
Currently no imaging modality is capable of image these nanoparticles and the surrounding tissues without disturbing the biological structure.
Metal oxide nanoparticles generate intense CARS signals due to large nonlinear susceptibility enhanced by two-photon electronic resonance of the band gap transition.

|
Gill Structure
Fish gills give information on the affect of biological particles on sensitive biological structures, can be used to indicate the presence of nanoparticles in the environment.
On each side of the fish there are four gill arches (a), bearing double rows of elongated, laterally projecting structures, gill filaments (b).
The lamella (c) are composed of two parallel sheets of epithelia separated by a narrow space through which blood circulates.
|
| Forwards- vs Epi-CARS
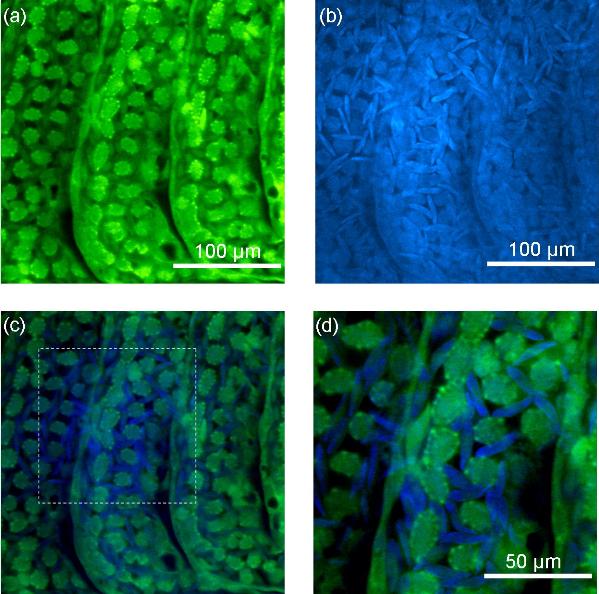
Figures (a) and (b) compare E-CARS and F-CARS images of the normal structure within the gills.
Stokes and pump wavelength were 1255 nm and 924 nm respectively, providing contrast of CH rich structures.
F-CARS image show high contrast of RBCs against the lamellae structure. In E-CARS RBCs are barely visible. Difference is due to spatial dependence of CARS generation.
Combining E- and F-CARS provides excellent visualistion of the microvasculature structure within the secondary lamellae and its interaction with the RBCs. Figures (c) & (d) shows the epi- (green) and forward-CARS (blue) data from (a) and (b) combined in a single image.
| |
3-Dimensional Imaging of Nanoparticles
Z-stack of 320 depth-resolved slices separated by 0.25 microns.
Figure (a): Multiplanar Reformated z-stack
YZ cross-section - vertical dotted line.
XZ cross-section - horizontal dotted line.
Aggregate of nanoparticles located in blood channel. (Indicated by arrows)
Figure (b) 3D projection of z-stack
Green = Forward-CARS
Blue = Epi-CARS

| |
Back to top



